A domain name is the online home address where you will build your website. Without a domain name, your website has no identity.
When someone visits your website, they access your domain name, and then the domain name is pointing to it.
Having a thorough understanding of domain names is really important. In this article, we will learn about What Is A Domain Name and how it works.
Table of Contents
What Is A Domain Name? What Is DNS?
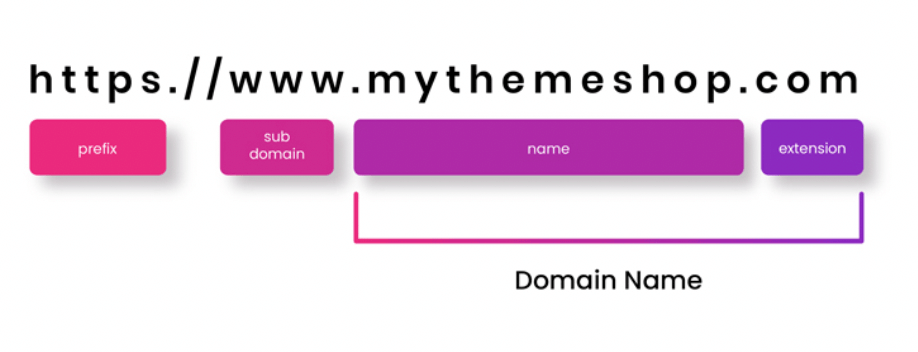
In simple words, a domain name is a string of words used for accessing a website. Those sting of words map to a certain IP address to pull the information you need from a client network computer called a web server.
The internet is a network of tons of giant computers connected using a global network of cables. A domain name is an online identity for you in this internet world.
A domain name tells the DNS ( Domain Name Server) from which computer your website files should be fetched. All domain names point to an IP address, basically the remote computer’s address.
The funniest thing is that the internet does not know what is a domain name. It can only recognize IP addresses.
So basically, when you type the domain name, it redirects you to an IP address and displays the information.
Every computer in this internet network has an IP address. An IP address is the unique identity of that computer. For example, 192.162.0.1 is an IP address.
You can also think of a domain name as a phone book where the domain name is the person’s name and the IP address is that person’s phone number.
Why do we need a phone book? Because it’s not easy to remember all the numbers. Right? Similarly, we use domain names because it’s not easy to remember all IP addresses.
A domain name is also called a URL ( Uniform Resource Locator). A URL is nothing but the address of a resource on the internet.
Difference Between Domain Name And Web Hosting
Often, we are confused between a domain name and web hosting. We think that both are the same. But in reality, both are two different things.
Consider the domain name as your home address, and when you build a website using web hosting, it becomes your home.
Web hosting is where all your website files reside. When you enter a domain name in the browser, it connects to the name server, which then connects to the IP address of the remote computer and gives you the information you want.
You need a domain name and web hosting to create a website. You can buy services from the same vendor, like Hostarmada, or from separate vendors.
Domain name + Web hosting -> A running website
To connect your domain name with your web hosting service, you need to use a name server that connects to your web server’s IP address.
Domain Name -> DNS-> Name Server -> IP Address
Why A Domain Name Is Required?
Like, it is impossible to remember phone numbers, and similarly, it is next to impossible to remember IP addresses. That is why a domain name is important just for our convenience.
For example, consider there is no domain name. In that case, what would have happened? You must enter the IP addresses whenever you want to access a website. That would have been a disaster.
The domain name also helps in securing your website. If the IP address is available in public, anyone can try to hack your website because they will get the remote computer’s location. You can also use CDN to mask your IP addresses.
How Does A Domain Name System Work?
As I told you before, a domain name is nothing but a masked address of your website server. Since memorizing IP addresses is not possible, we use a domain name.
When you type a domain name in the browser, it sends a query to the global network of servers or domain name servers ( DNS). The DNS then looks for the correct nameserver against that particular domain name.
If DNS finds that nameserver, it redirects the domain name to that name server. And that name server then redirects to the IP address of the remote computer.
That remote computer then delivers the requested information and displays it on the browser.
So here are the things that happen in the background when you type a domain name in the browser.
- Type a domain name in the browser
- The browser sends a signal to the DNS
- DNS looks for the correct name server
- Name servers redirect to the IP address of the remote computer
- The remote computer fetches the file and delivers it to you.

Types Of Domain Names
There are different types of domain names based on the domain extensions.
- Top Level Domain Names ( TLD)
- Country Code Top Level Domain Names ( ccTLD)
- Sponsored Top Level Domain Names ( sTLD)
Top Level Domain Names ( TLD)
Domain extensions like .com, .net, .org, and .io are top-level domain names. Hundreds of top-level domain names are available, but .com is the most popular, accounting for about 37% of all domain names.
Country Code Top Level Domain Names ( ccTLD)
Domain extensions that are specific to some countries are called country code top-level domain names, for example, .in, .us, .uk, etc.
Sponsored Top Level Domain Names
Sponsored top-level domain names are used by a sponsor representing a specific community to serve a particular audience category.
For example, .gov is for government websites, and .edu is for educational websites. You can not simply buy those domain extensions unless you prove that you belong to those types of organizations.
Who Is Responsible For The Domain Name System?
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) manages the domain name system. They create and manage roles and regulations for the domain name system.
If you want to buy a domain name, you cannot directly buy from ICANN. Instead, you need to buy from domain registrars who are nothing but authorized resellers for ICANN.
Domain registrars rent the domain name, manage the domain information, and update the domain information as and when required. In return, they charge a nominal fee every year.
Please note that you can never buy a domain name, but you can only get it on rent. What does that mean, every year you have to renew your domain name by paying the rent.
How To Choose A Domain Name
There are certain best practices that you should follow while choosing a domain name so that you can get the best out of it.
- Always try to get the .com extension
- Try to buy a brandable domain name rather than a generic domain name
- Avoid domain names with numbers or symbols
- Use niche keywords in the domain name
- Choose a domain name that is easy to spell
- Choose a domain name that is easy to pronounce
- Use short domain names
- Don’t copy other domain names.
Conclusion: What Is Domain?
After reading this article, I hope you got a good idea about domain names. A domain name is the first thing that you will choose when you start an online business.
So make sure it is unique, brandable, and reflects the root of your business. Changing a domain name is not as easy as it sounds.
It has some serious consequences. So, choosing the best before you venture into online business is better.
FAQ: What Is A Domain Name?
What Is A Subdomain?
A subdomain is an extension of the main domain. Once you buy the main domain, you can create the subdomain yourself.
For example, rianstech.com is the main domain, whereas blog.rianstech.com is a subdomain.
Subdomains are used to categorize your website content.
Can I Move My Website To A Different Domain?
Yes, you can always move your website to a different domain. You can follow this article to learn how to move your website
Can I Sell A Domain Name?
You can sell a domain name whenever you want.
What Is Domain Privacy Protection?
Domain privacy protection is a service many domain registrars offer to safeguard your personal information from going public. This is a must-have add-on for all domain names.
Can You Buy A Domain Name Forever?
No, you can not buy a domain name forever. You can buy a domain name for up to 10 years.
Will Changing Domain Name Affect SEO?
Yes, it does if you don’t set 301 redirects properly to redirect traffic from the old domain name to the new domain name.
What Happens When A Domain Name Expires?
Once a domain name expires, you will get 30 days of buffer time to renew it. If you fail to renew it even in the buffer time, the domain name will be available for the public to buy.