Google (or other search engines) does not know what your website is about. For search engines to know about the content of your website, you need to submit some information to search engines.
But how do we do that?
Sitemaps! Yes, with a sitemap, a search engine can discover the contents of your website and crawl accordingly.
Creating a sitemap is one of the many ways of optimizing a site for SEO. It helps visitors and search engine bots understand your website’s structure better.
Sitemaps offer a better user experience for visitors and accurate information in a structured way for search engine bots to crawl.
This article will discuss the different types of sitemaps, how to use sitemaps to optimize your website, and how to create a sitemap in WordPress.
What Is A WordPress Sitemap?
As the name suggests, a sitemap is the complete link map of your site. This file contains all the public URLs of your website. You can control the links that need to be included in a sitemap.
By default, WordPress does not create sitemaps. You must manually create one or use WordPress plugins to do that for you.
A sitemap is like a blueprint containing links to all your pages, posts, images, and other stuff you want to include. You will need to create different sitemaps for different types of content.
Why Sitemaps Are Important
Either a new site or an old site, Google (or other search engines) discovers the content of your website by following internal links.
If you have a sitemap with all links to your website, you are basically making Google’s job easier. Google can easily find the structure and links of your website and crawl them accordingly.
Websites with sitemaps get crawled quickly and easily compared to ones that do not have a sitemap.
Here are the different scenarios where sitemaps are really important.
Easy Navigation
A visual sitemap shows your website’s structure and hierarchy, helping visitors easily navigate through different pages. This improves the overall experience and visitor retention.
Search Engine Optimization
When Google finds your website content easy to crawl, it may rank you higher in the search engine result pages.
On the other hand, if visitors find it easy to navigate through using sitemaps, they will prefer to come back to your website. So you will benefit from both options.
Better Crawlability
Google hates if your website does not have a sitemap, as it has to do a lot of work to crawl it. By providing a sitemap, you are making Google happy. Thus, Google (or other search engines) will crawl and index your website links faster.
Types Of Sitemaps
Usually, sitemaps are categorized into two types.
- XML Sitemap [Extensible Markup Language]
- HTML Sitemap [HyperText Markup Language]
Both types play a significant role in optimizing a website but in different ways. XML sitemaps are machine-readable sitemaps meant for search engines, whereas HTML sitemaps are visual sitemaps meant for human visitors.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is usually created for search engines. It contains URLs for all your blog content and other information, such as when the content was created and modified, how many images are in the content, etc.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is machine-readable language useful for search engines to crawl your website content easily and quickly
Though the XML sitemap is accessible to common visitors, it’s of no use to them. The search engine crawler detects the XML sitemap and crawls all links available in it.
In WordPress, you can create sitemaps for different content, such as posts, pages, images, categories, etc. When content changes, XML sitemap files are also updated so that search engines can crawl the updated content.
Benefits Of XML Sitemap
The main benefit of an XML sitemap is that it helps crawl your website content easily.
There is no guarantee that all links on the website will be crawled and indexed, but at least Google will be aware of your website’s content.
One more benefit is that once your website content is updated, the same gets updated in the sitemaps and eventually crawls.
An XML sitemap is also useful for letting Google or other search engines know about your blog’s media content, as WordPress creates a separate sitemap for all media content, such as images and videos.
How To Create An XML Sitemap Using Rank Math
Using Rank Math, creating an XML sitemap is very easy. Follow the instructions below, and you’ll be good to go.
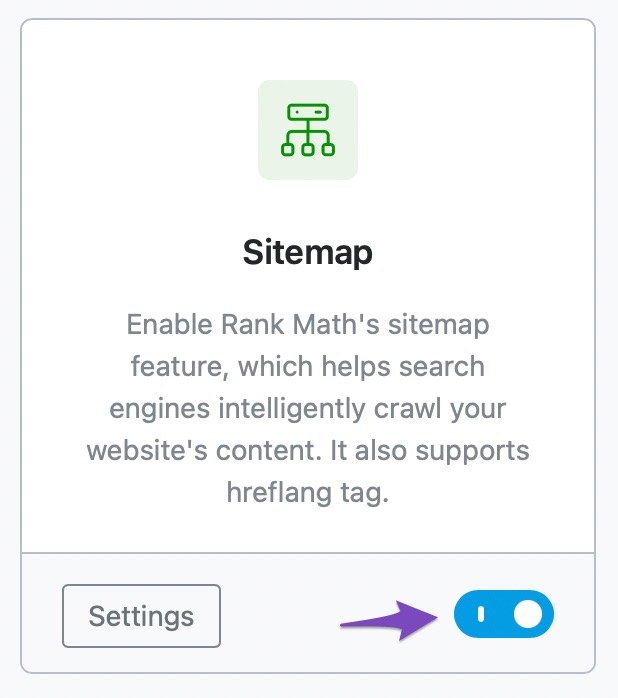
1. Enable Sitemap In RankMath Dashboard
First, you must enable “Sitemap” from the Rank Math dashboard and then access the Rank Math settings.
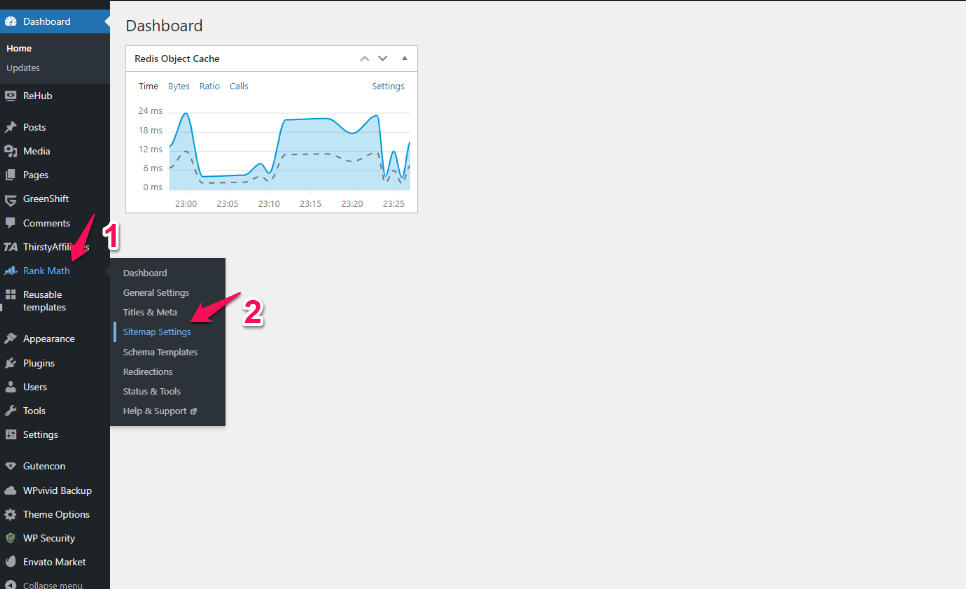
2. Access RankMath Settings
To access Rank Math Sitemap setting, you can click on RankMath -> Sitemap Setting
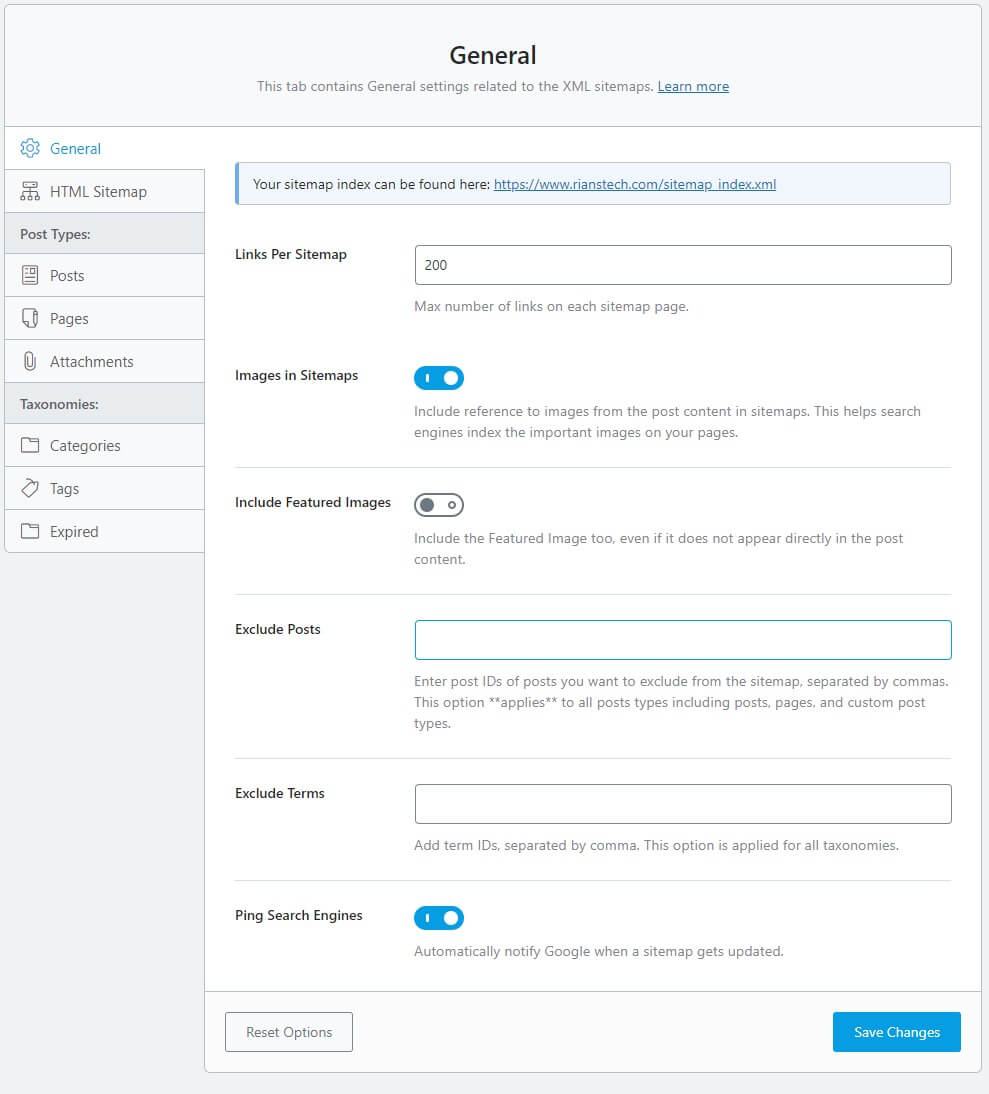
3. Configure General Settings
Once you click on Sitemap Settings, you will be shown the window below. Under General, you can change the following settings.
Your sitemap URL will be shown at the top of the window. The same you need to copy and submit to search engines.
- Links Per Sitemap: Keep it default at 200
- Images In Sitemaps: Yes
- Include Featured Image: No ( Featured images do not add any value)
- Exclude Posts: Here, you can enter the post IDs that you want to exclude
- Exclude Terms: Her,e you can exclude posts with any terms
- Ping Search Engines: Yes
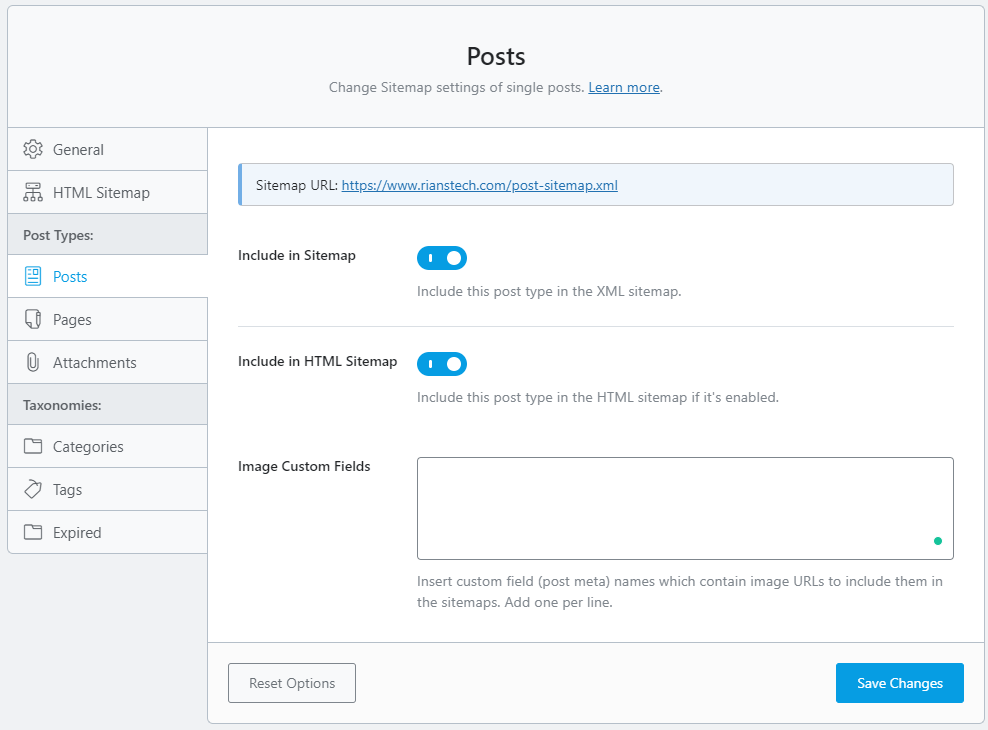
4. Configure Other Individual Settings
You can go to the individual settings page for each item listed on the left side and change the settings accordingly. For example, the image below shows the setting page for “Posts.”
Here is the snippet of what RankMath XML sitemaps look like.
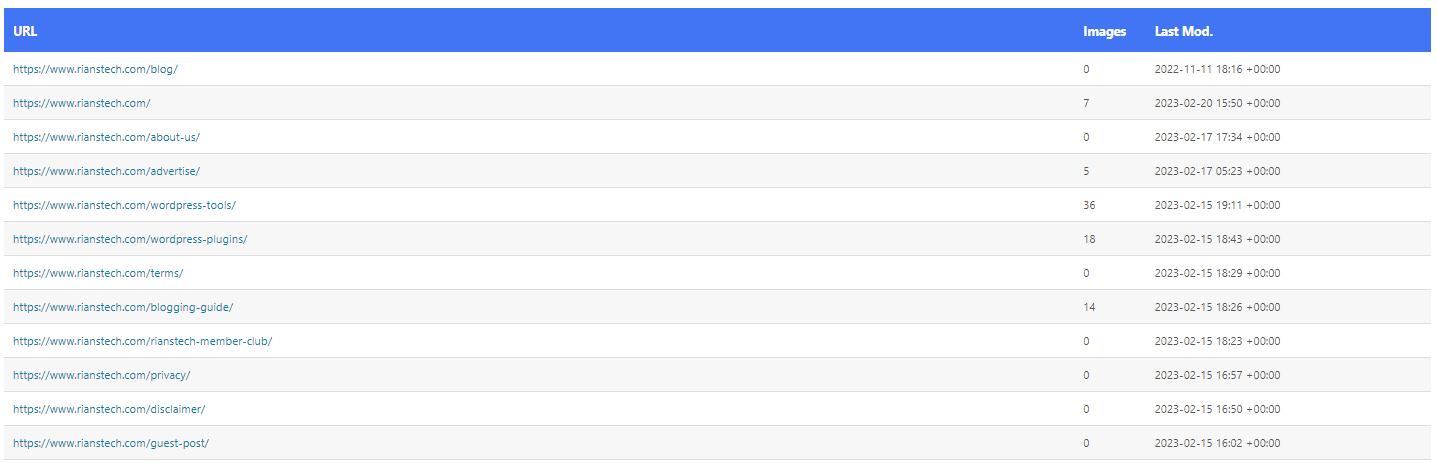
How To Submit XML Sitemaps To Google
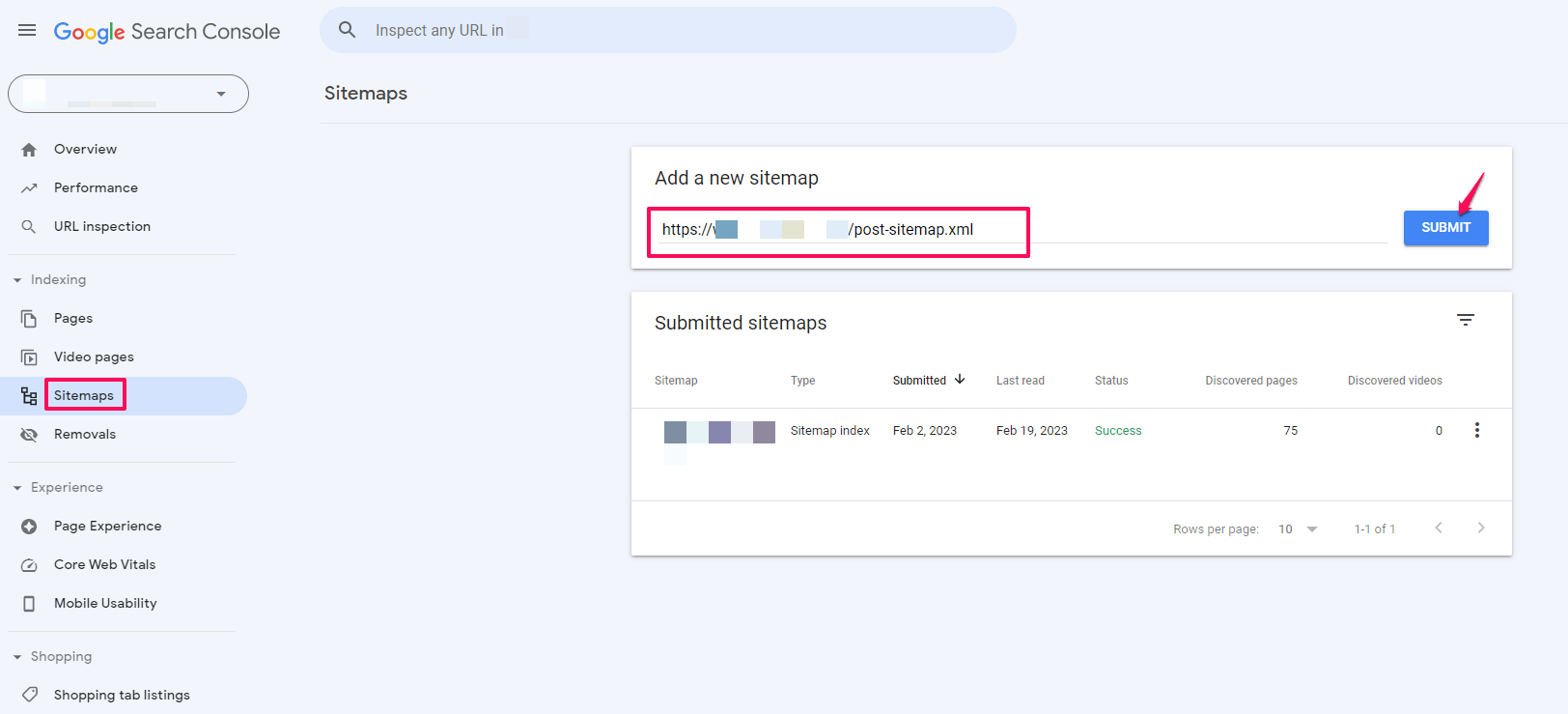
Here are the processes you can follow to submit a sitemap to Google.
- Login to Google Search Console
- Click on” Sitemaps” on the left navigation bar
- Enter the sitemap URL
- Click Submit
HTML sitemap
Unlike XML sitemaps, which are purely for search engines, HTML sitemaps are for general visitors. They help them navigate your website easily and give an overview of your website content along with links so that they can access their preferred content.
Benefits Of HTML Sitemaps
Although HTML sitemaps do not impact SEO or overall blog visibility, they add value to your website. Visitors will be pleased to see all content links on one page instead of browsing all pages and categories.
How To Create An HTML Sitemap Using Rank Math?
Creating an HTML sitemap using Rank Math is easy, like creating an XML sitemap. Here are the steps to follow.
You must enable Sitemap in the Rank Math dashboard and access the RankMath settings. Steps 1 and 2 explain the process.
To access the HTML Sitemap under RankMath general settings, click on the option below.
You must “Check” on “HTML Sitemap” to enable the feature.
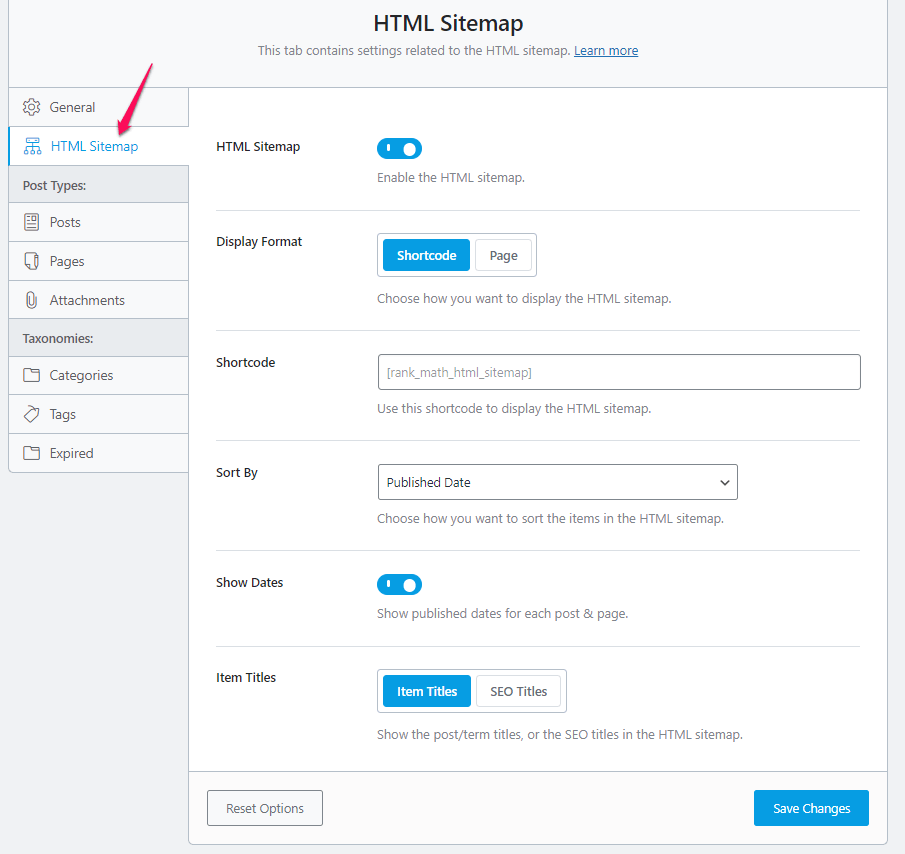
You can set the below option under the RankMath HTML Sitemap settings page.
- Display Format: Using the short code, you can show an HTML sitemap anywhere or choose a page to display.
- Sort By: You can sort by Published Date, Modified Date, Alphabetical, or using Post IDs
- Show Date: If you want to show the dates next to the post, check the option here.
- Item Title: You can choose the item or SEO title in the HTML sitemap.
Here is a snippet of the RiansTech HTML sitemap with the above settings.
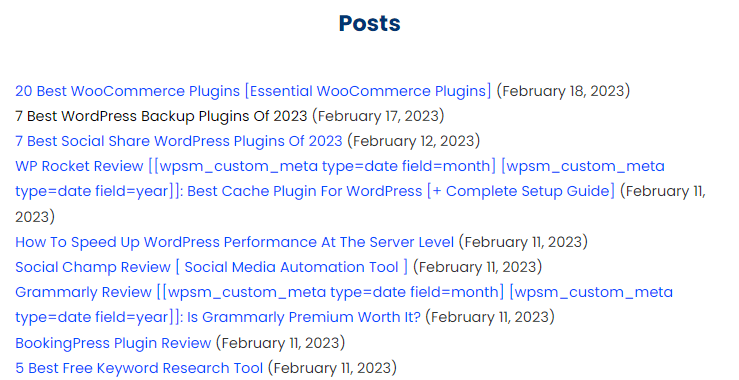
Do I Need To Use Both Types Of Sitemap?
I would prefer to use both, as an XML site map is a must for search engines, and an HTML sitemap is good for visitors. Having both sitemaps will add value to your website in terms of search appearance and credibility.
Conclusion: How To Create A Sitemap In WordPress
A sitemap is a must nowadays if you want to rank your blog in search results. Hopefully, this article will give insight into sitemaps and their benefits.
That’s all I have in this article. Hopefully, you got some useful information from it. If you have any questions, then do write in the comment section, and I will be happy to answer them.